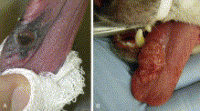
Oral Tumors
• Melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and fibrosarcoma are the most common malignant oral tumors in dogs; SCC is the most common feline oral malignancy, by far
• Approximately 5% of oral tumors in dogs are benign dental tumors (epulides)
• The presence of loose teeth in a patient with otherwise good dentition warrants a search for oral neoplasia
• Obtain incisional biopsies from sites that can be easily excised at the time of definitive surgery (i.e., lesions should be approached from within the oral cavity)
Salivary Gland Tumors
• The majority of canine and feline salivary tumors are malignant, with adenocarcinoma the most frequent diagnosis.
• Metastasis at the time of diagnosis is more common in cats than dogs and may develop in the regional lymph nodes and other distant locations late in the course of disease
• Local recurrence is common with surgical excision alone